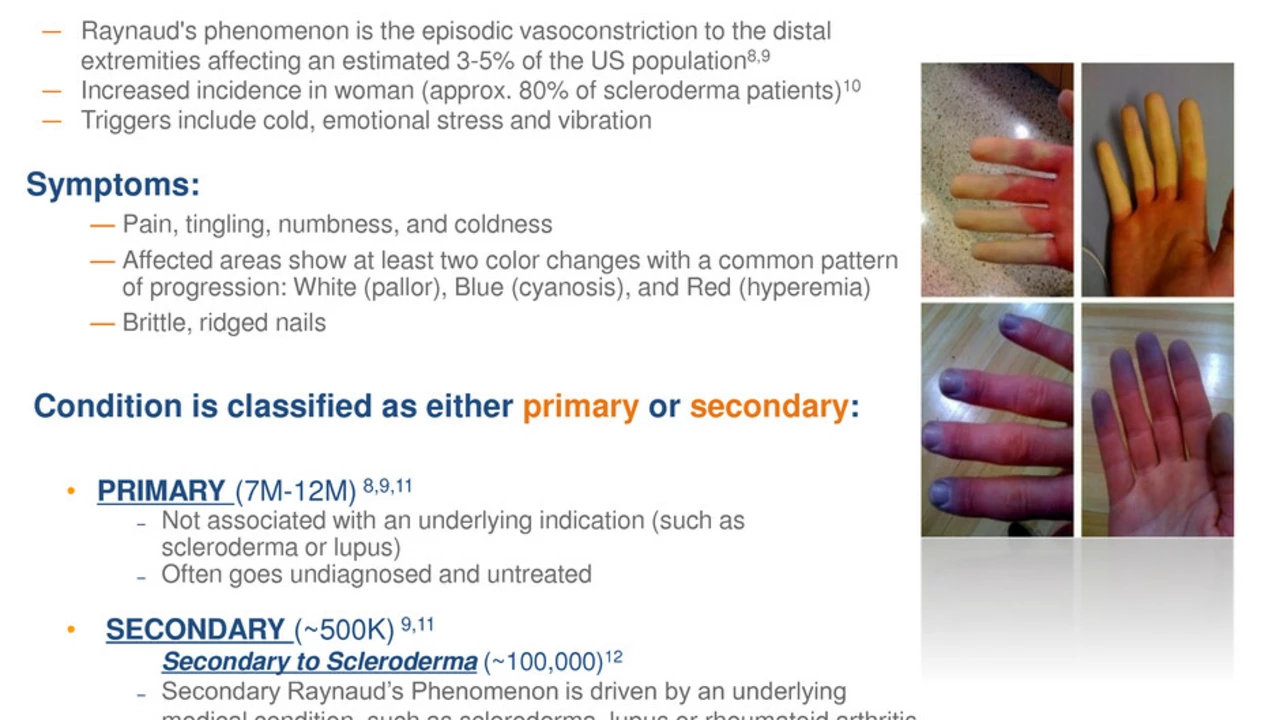
Understanding Raynaud's Phenomenon
Raynaud's phenomenon is a condition that affects your blood vessels, primarily in your fingers and toes. It is characterized by episodes of color changes in your skin in response to cold or stress, with the skin turning white or blue and then red as blood flow returns. These episodes can be quite painful and for some people, they can be debilitating. There are two forms of this condition: primary Raynaud's, which is the most common, and secondary Raynaud's, which is more severe and is linked to other health conditions.
Existing Treatment Options for Raynaud's Phenomenon
Currently, the treatment of Raynaud's phenomenon is mainly focused on preventing episodes and reducing the severity of symptoms when they do occur. This can include lifestyle changes such as avoiding cold temperatures, wearing warm clothing, and refraining from activities that could cause an episode. Medications are often prescribed to help widen blood vessels and improve blood flow. However, these treatments don't always work for everyone, and they can have undesirable side effects.
Introduction to Clonidine: A Different Approach
Clonidine is a medication that is primarily used to treat high blood pressure. It works by stimulating receptors in the brain that decrease the speed and force of the heartbeat, thereby reducing blood pressure. Interestingly, because of its effects on the circulatory system, it has been suggested as a potential treatment for Raynaud's phenomenon.
How Clonidine Works for Raynaud's
Clonidine works in Raynaud's phenomenon in a similar way to how it works for high blood pressure. It stimulates the alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the brain, which leads to a decrease in the overall resistance of blood vessels. This can help to improve blood flow in areas affected by Raynaud's, reducing the severity and frequency of episodes.
Research on Clonidine and Raynaud's Phenomenon
Several studies have been conducted to investigate the potential benefits of clonidine for people with Raynaud's phenomenon. The results have been promising, with many patients reporting a decrease in the frequency and severity of their episodes. However, more research is needed to fully understand the potential benefits and risks of this treatment option.
Potential Side Effects of Clonidine
As with any medication, clonidine comes with potential side effects. These can include dry mouth, drowsiness, constipation, and a decrease in blood pressure. It's important for patients to discuss these potential side effects with their healthcare provider before starting treatment.
Clonidine as an Adjunct Treatment
Given the potential side effects, clonidine may not be suitable as a first-line treatment for Raynaud's phenomenon. However, it could be a useful adjunct treatment for patients who are not responding to other therapies, or for those who cannot tolerate the side effects of other medications.
Personal Experiences with Clonidine
In this section, we will share personal experiences from people who have used clonidine for Raynaud's phenomenon. These stories can provide valuable insights into what it's like to use this medication, and can help others make informed decisions about their own treatment options.
Conclusion: A Potential New Treatment Option
In conclusion, while clonidine is not currently a standard treatment for Raynaud's phenomenon, it holds potential as a new option for patients who are not responding to other treatments. As with all medications, it's important for patients to discuss the potential benefits and risks with their healthcare provider. With further research and clinical trials, we may be able to further understand the potential of clonidine for treating Raynaud's phenomenon.

Monika Pardon
July 21, 2023
Oh sure, because the government didn’t already patent clonidine for mind control.
Rhea Lesandra
July 21, 2023
If you’re exploring new options for Raynaud’s, keep an open mind and stay proactive.
Clonidine’s mechanism of reducing central sympathetic outflow can theoretically improve peripheral blood flow.
Clinical studies, though limited, have reported fewer attacks and milder discolorations in some patients.
Don’t let the occasional dry mouth or drowsiness deter you from discussing it with your physician.
A gradual titration schedule often minimizes side‑effects while preserving the therapeutic benefit.
Remember that lifestyle measures-warming your hands, stress reduction, and avoiding nicotine-remain foundational.
Combine medication with these habits for a synergistic effect that may enhance outcomes.
If you have comorbid hypertension, clonidine may actually serve a dual purpose, addressing both issues.
Always monitor your blood pressure when starting, especially if you’re on other antihypertensives.
Keep a symptom diary; noting the frequency, intensity, and triggers of attacks can guide dosage adjustments.
Don’t hesitate to reach out to support groups; shared experiences often reveal practical tips.
Your healthcare team can order a trial period to assess efficacy before committing long‑term.
Patience is key, as it may take several weeks to notice a meaningful reduction in episodes.
If after an adequate trial you see no improvement, there are alternative agents such as calcium channel blockers or phosphodiesterase inhibitors.
Stay hopeful, stay informed, and keep advocating for your own comfort and health.
Kasey Marshall
July 21, 2023
Clonidine does affect alpha‑2 receptors reducing peripheral resistance it could help but data is still limited.
Dave Sykes
July 22, 2023
Look, if you’ve tried the usual vasodilators without success, adding clonidine under supervision is worth a shot. It’s not a first‑line drug, but the evidence suggests it can blunt severe attacks when other meds fail. Talk to your doctor about a low‑dose trial and monitor BP closely.
Erin Leach
July 22, 2023
I hear you, dealing with painful episodes can be exhausting, remember you’re not alone, many people find relief with small adjustments and supportive care, keep tracking your symptoms and stay in touch with your healthcare team.
Erik Redli
July 22, 2023
This is nonsense, clonidine will just drop your blood pressure dangerously, stay away from a drug that can cause severe hypotension.