Understanding Urinary Retention
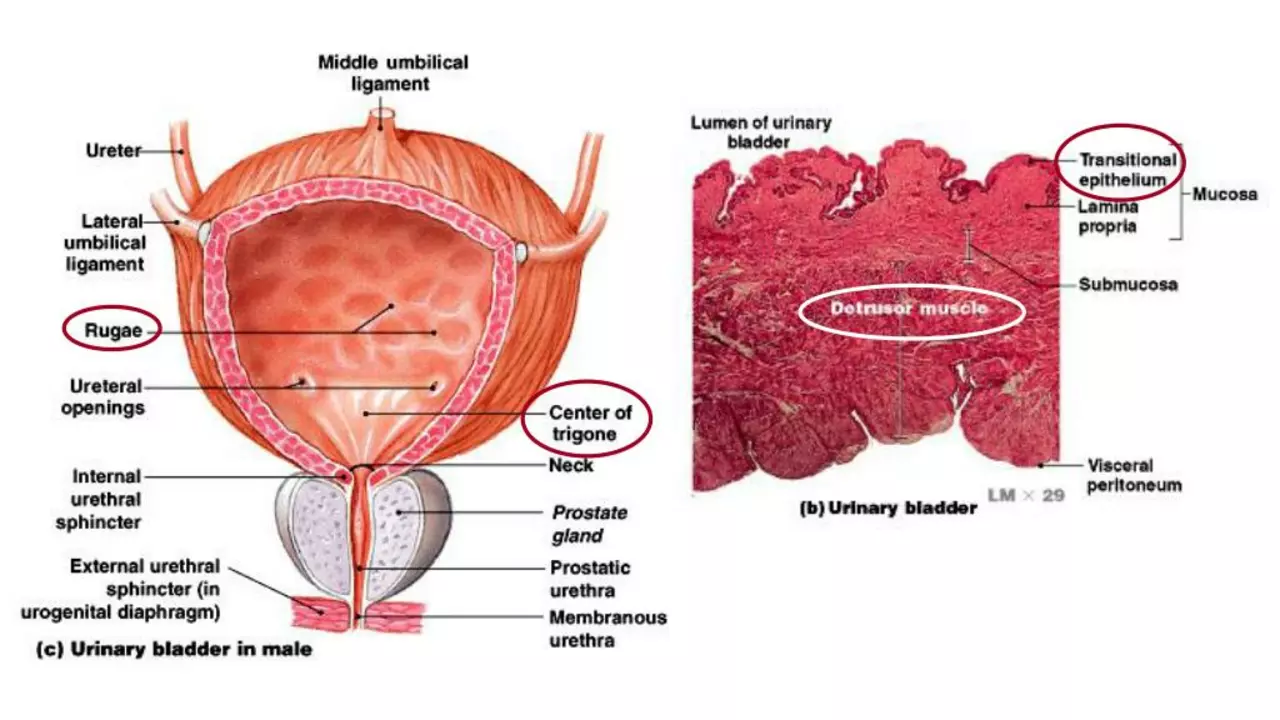
The first step in understanding the relationship between urinary retention and bladder cancer is to delve into what urinary retention actually is. Urinary retention is a condition where one is unable to completely empty the bladder. It can be acute, which is a sudden inability to urinate causing great discomfort, or chronic, which is a long-term problem that can be less noticeable due to its slow progression. The causes of urinary retention vary, including factors like nerve problems, certain medications, and underlying medical conditions.
Exploring Bladder Cancer
Now, let's delve into what bladder cancer is. Bladder cancer is a common type of cancer that begins in the cells of the bladder, the organ that stores urine. It can develop at any age, but it's more common in older adults and in individuals who smoke or are exposed to certain chemicals. The signs and symptoms of bladder cancer can include blood in the urine, pain during urination, frequent urination, and back pain.
How Urinary Retention Could Lead to Bladder Cancer
The link between urinary retention and bladder cancer is not direct, but it exists. Chronic urinary retention, in particular, can lead to a series of complications, one of which is an increased risk of bladder cancer. Constant pressure on the bladder walls caused by retained urine can lead to cell mutations which might develop into cancerous cells.
Identifying the Symptoms of Both Conditions
Recognizing the symptoms of both urinary retention and bladder cancer is crucial. The signs of urinary retention include difficulty starting to urinate, weak or interrupted urine flow, an urgent need to urinate with little success, and feeling the need to urinate after finishing urination. On the other hand, the symptoms of bladder cancer include blood in urine, frequent urination, painful urination, back pain, and pelvic pain.
Diagnosing Urinary Retention and Bladder Cancer
Both urinary retention and bladder cancer are diagnosed using a variety of tests. For urinary retention, a physical examination, postvoid residual measurement, and urinary flow test are typically conducted. For bladder cancer, urine lab tests, cystoscopy, and imaging tests such as CT scans are common. Early detection is key to successful treatment, so regular check-ups are crucial, especially if you have any of the symptoms or risk factors.
Treatment Options for Urinary Retention and Bladder Cancer
The treatment for urinary retention depends on the underlying cause. It can include medications, catheterization, or surgery. On the other hand, treatment for bladder cancer also depends on the stage of the cancer, overall health, and treatment preferences. It may involve surgery, immunotherapy, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or a combination of these treatments.
Living with Urinary Retention and Bladder Cancer
Living with urinary retention or bladder cancer can be challenging. However, with the right treatment and support, it's possible to manage these conditions and maintain a good quality of life. It's essential to follow the treatment plan recommended by your healthcare team, maintain a healthy lifestyle, and seek support from friends, family, or support groups.
Preventing Urinary Retention and Bladder Cancer
While not all cases of urinary retention and bladder cancer can be prevented, certain lifestyle changes can reduce the risk. These include quitting smoking, staying hydrated, maintaining a healthy weight, and following a balanced diet. Regular check-ups are also crucial to detect any potential issues early.

Jennyfer Collin
July 16, 2023
It appears that the prevailing discourse on urinary retention and bladder carcinoma conveniently omits the clandestine interests of pharmaceutical conglomerates. One must consider that the selective emphasis on certain risk factors may serve to divert attention from iatrogenic contributors. The mechanisms described herein could potentially mask the long‑term effects of proprietary medications that are seldom disclosed. 😊
Tim Waghorn
July 19, 2023
The correlation between chronic urinary retention and urothelial malignancies is indeed supported by epidemiological data. However, causality remains to be unequivocally established, as confounding variables such as smoking prevalence must be accounted for. Rigorous prospective studies employing standardized post‑void residual assessments would elucidate this relationship. Ultimately, a multidisciplinary approach is warranted.
Brady Johnson
July 23, 2023
Honestly, the article glosses over the grim reality that delayed diagnosis can be a death sentence for many patients. It's a travesty that the medical community continues to downplay the urgency. Wake up, people!
Jay Campbell
July 26, 2023
I appreciate the comprehensive overview and would add that patient education on early warning signs can dramatically improve outcomes. Collaborative care models have shown promise in managing both retention and oncologic surveillance.
Laura Hibbard
July 29, 2023
Ah great, another “comprehensive guide” that tells us we should watch out for blood in our pee – what a revelation! 🙄 Still, kudos for packing all the clichés into one article.
Rachel Zack
July 30, 2023
People should stop ignoring their health and start taking responsbility for the choices they make, like smoking and ignoring symptoms. It's not just about luck, it's about moral choices.
Lori Brown
August 3, 2023
Fantastic read! Keep spreading awareness – together we can catch problems early and improve lives :)
Jacqui Bryant
August 6, 2023
Staying hydrated really helps.
Paul Luxford
August 10, 2023
It's vital to maintain regular check‑ups, especially for those with risk factors, to ensure any issues are identified promptly.
Nic Floyd
August 13, 2023
From a urological perspective the pathophysiology implicates intravesical pressure dynamics leading to urothelial dysplasia risk elevation 📈 the synergy between chronic overdistension and carcinogenic exposure warrants further molecular interrogation 🚀
Johnae Council
August 14, 2023
Really? Another article that pretends to be groundbreaking while rehashing textbook facts. It's lazy content.
Manoj Kumar
August 18, 2023
One could argue that the universe is conspiring to keep us blissfully unaware of our own mortality, yet here we are, dissecting the minutiae of bladder pressure like philosophers debating the meaning of existence – how delightfully absurd.
Hershel Lilly
August 21, 2023
I wonder whether integrating urinary flowmetry data with cystoscopic findings could refine early detection algorithms. Such interdisciplinary efforts might bridge existing gaps.
Carla Smalls
August 25, 2023
You’ve got this! Remember, staying proactive with lifestyle adjustments and adhering to your treatment plan makes a huge difference. Keep pushing forward! 😊
Monika Pardon
August 28, 2023
Clearly, the omission of any mention of governmental oversight in this discussion is no accident; the powers that be prefer us to remain ignorant of the covert trials underway. But hey, who needs transparency when speculation is so entertaining?
Rhea Lesandra
September 1, 2023
First and foremost, let me commend everyone for engaging with such a critical health topic; awareness is the cornerstone of prevention. When we examine urinary retention, we must recognize that the bladder is not merely a passive reservoir but an active organ whose function reflects systemic health. Chronic retention imposes sustained intravesical pressure, which, over time, can induce epithelial irritation and cellular turnover. This cellular turnover, in turn, creates a fertile ground for mutagenic events, especially in the presence of carcinogens such as tobacco metabolites. Moreover, the inflammatory milieu generated by stagnant urine fosters oxidative stress, further compromising DNA integrity. It is also essential to appreciate that patient comorbidities – diabetes, neurologic disorders, and medication side effects – can exacerbate retention and mask early oncologic signs. Regular post‑void residual measurements provide an objective metric to monitor retention severity and guide timely interventions. Simultaneously, routine urinalysis, cystoscopy, and imaging should be incorporated into surveillance protocols for high‑risk individuals. Lifestyle modifications, including smoking cessation, adequate hydration, and weight management, serve as powerful adjuncts to medical therapy. Collaboration among urologists, primary care physicians, and oncology specialists ensures a coordinated approach that addresses both functional and malignant aspects of bladder health. Education initiatives that empower patients to recognize hematuria, dysuria, and changes in urinary patterns can dramatically reduce diagnostic delays. In the era of precision medicine, emerging biomarkers hold promise for earlier detection of urothelial neoplasia, potentially revolutionizing outcomes. While we acknowledge that not every case of retention leads to cancer, the cumulative evidence underscores a non‑trivial association that warrants vigilance. Let us therefore advocate for comprehensive screening guidelines that reflect this nuance, and encourage research funding aimed at elucidating the molecular pathways involved. By integrating clinical vigilance with scientific inquiry, we pave the way for improved prognosis and quality of life for those affected. Together, we can transform uncertainty into proactive care, and ensure that the bladder receives the attention it deserves.
Kasey Marshall
September 4, 2023
Check your flow numbers stay within normal limits and get screened if you notice blood in urine