Pharmacology made useful: quick guides to drugs you’ll actually meet
What if one drug history tells you how treatment changed and another explains why a medicine can help — and harm — at the same time? This Pharmacology category on KwikMed gives short, practical posts that answer the real questions: how a drug works, when clinicians use it, and what to watch for.
Quick drug highlights you can apply
Amiodarone — a drug that came from angina research but became a mainstay for serious heart rhythm problems like atrial fibrillation and ventricular arrhythmias. It works well, but it sticks around in the body and can affect the thyroid, lungs, and liver. If you or someone you care for is starting amiodarone, expect baseline tests (thyroid, liver) and periodic follow-up. Newer alternatives exist, but amiodarone still matters when other drugs fail.
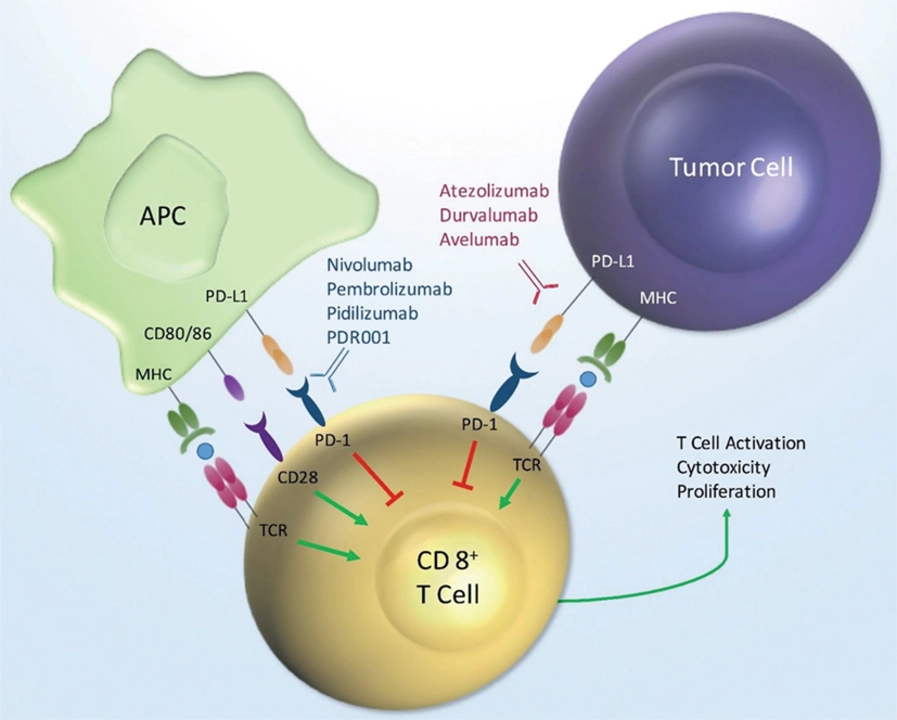
Cyclosporine — this one’s about control. Cyclosporine binds cyclophilin and blocks calcineurin, which quiets T-cells. That makes it a go-to for preventing organ rejection and treating some autoimmune diseases. The trade-offs are clear: watch kidney function, blood pressure, and many drug interactions. Measuring blood levels helps keep dosing safe.
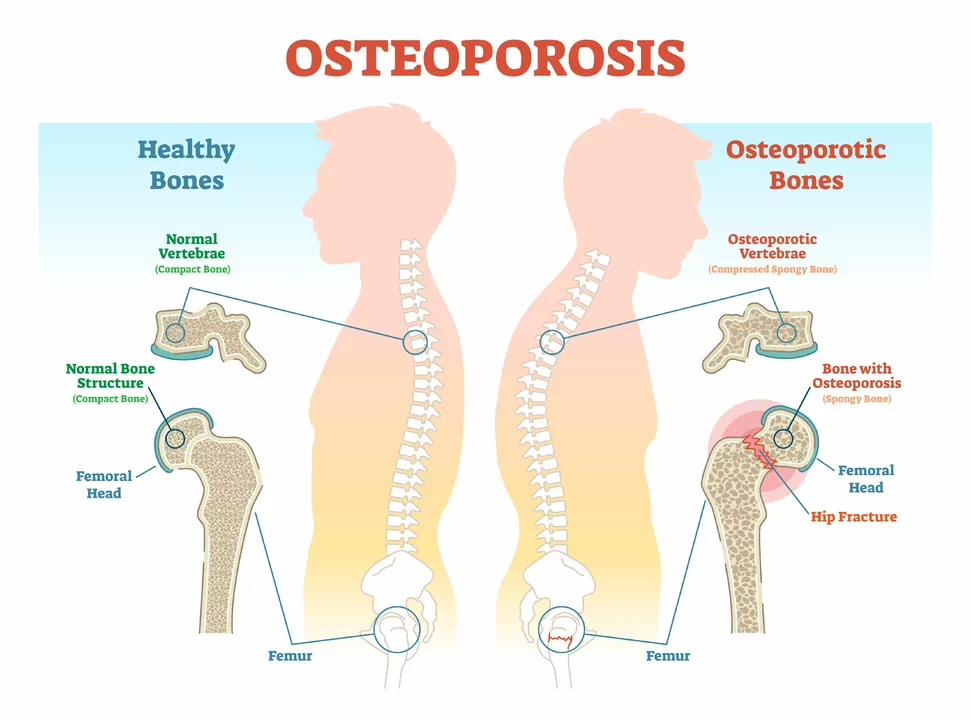
Secondary hyperparathyroidism and osteoporosis — not a drug, but a key connection. When the body raises parathyroid hormone (often because of chronic kidney disease), bones give up calcium and get weaker. Treating the cause (vitamin D, controlling phosphate, and sometimes calcimimetics) lowers fracture risk. If you’re tracking bone health, check bone density and talk about labs that show PTH and calcium balance.
Cefuroxime — a second-generation cephalosporin often used for community-acquired pneumonia. It covers common lung bugs and penetrates lung tissue well. There are oral and IV options; choice depends on illness severity. Allergy to penicillin or cephalosporins and local resistance patterns will influence whether cefuroxime is a good pick.
How to use these posts
Read the short posts when you need focused answers: history to get context, mechanism to understand why side effects happen, and practical notes for monitoring. Use the keywords in each post if you want quick searches (for example: “amiodarone monitoring” or “cyclosporine interactions”).
I try to keep each article actionable: what the drug treats, how it works in one sentence, main side effects, and simple monitoring steps. None of this replaces your doctor’s advice — but it will help you ask better questions at the clinic or pharmacy.
Want more detail on a topic? Click the article that matches your question and look for sections on dosing, testing, and alternatives. If you’re managing a condition, bring lab results or a current medicine list when you talk to your clinician — that makes the conversation faster and safer.
Find clear, short guides here: history, mechanism, real-world uses, and safety tips for drugs you’ll encounter. Read one post, learn something useful, and feel better prepared for the next medical decision.